The EU AI Act is the European Union’s landmark law designed to regulate artificial intelligence systems in a way that protects people’s rights, promotes innovation and sets a global standard for AI governance. From bans on high‑risk autonomous technologies to sweeping new compliance requirements for AI providers worldwide, this regulatory framework is reshaping how AI is developed, deployed and governed.
Understanding the latest EU AI Act news today isn’t just important for tech professionals in Europe it matters to global businesses, developers, policymakers and citizens alike because the Act’s reach extends beyond EU borders to any company whose AI reaches EU users. As deadlines approach and reforms are proposed organizations are adjusting strategies, lawmakers are listening to critics and stakeholders and real‑world enforcement is beginning to take shape.
In this long‑form guide, you’ll find a clear, expert overview of current developments, what they mean for different stakeholders and where the EU AI Act stands right now in its phased rollout.
Understanding the EU AI Act
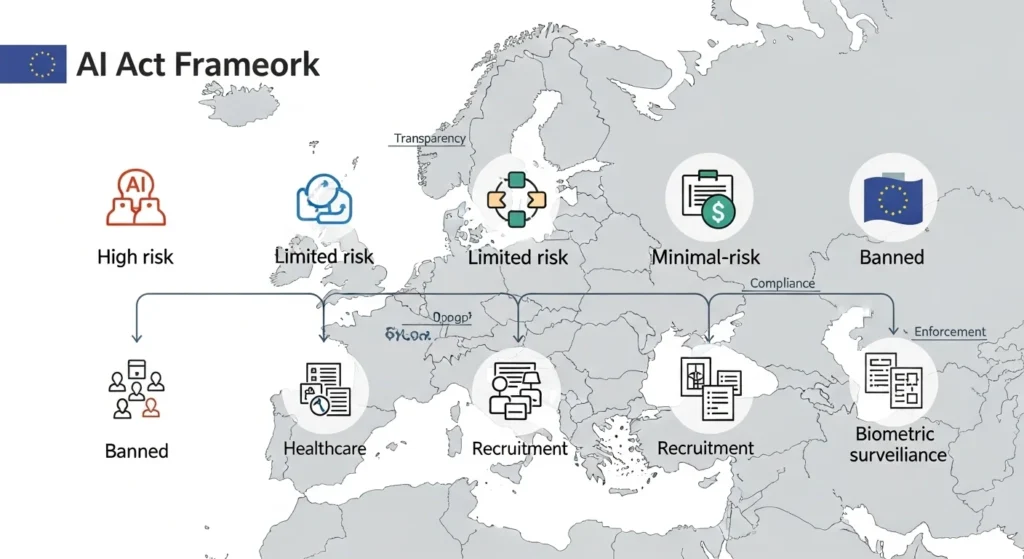
The EU AI Act is a comprehensive artificial intelligence regulation adopted by the European Union aimed at governing AI systems based on their risk level and societal impact. Instead of regulating all AI uniformly, it categorises AI into unacceptable risk, high risk, limited risk and minimal risk categories and applies rules that match the potential harm each poses.
This risk‑based approach allows the EU to balance innovation and safety. Systems that could pose serious dangers—like discriminatory automated decision‑making or unchecked biometric surveillance are outright banned, while others face structured compliance requirements. Importantly, the Act applies broadly: any AI system “placed on the EU market” or whose outputs are used within the EU must comply, regardless of where the developer or user is located.
The Act entered into force in August 2024 and is being phased in through multiple deadlines. Organizations across industries, from healthcare to finance to tech platforms, must now assess how and when the rules apply to their practices.
Why the Latest EU AI Act News Today Matters
At its core, the EU AI Act represents a global experiment in how democratic societies govern powerful technologies. It matters because:
- It sets expectations for AI safety, accountability and transparency that may become de facto international standards.
- It affects companies and developers worldwide, not only within the EU, due to its extraterritorial reach.
- It influences investment decisions, product planning, and market access for emerging AI technologies.
- It signals how future governance of digital systems might look in a world increasingly shaped by algorithms and automation.
Each new update in EU AI Act news today can change compliance strategies, affect risk planning and reshape innovation pathways for stakeholders everywhere
Latest Developments: What’s New in EU AI Act News Today
New Obligations for High‑Risk AI Are Now in Effect
As of today, preparatory obligations related to high‑risk AI systems have come into force in the EU. These obligations require organisations that place high‑risk AI on the market or use such systems within the bloc to begin fulfilling documentation, governance and compliance readiness measures. This marks a significant step in moving beyond planning into tangible enforcement.
These systems include those used in critical societal functions like healthcare diagnostics, employment screening tools, credit scoring and public services. The goal is to ensure that potential harms to health, safety and fundamental rights are properly managed well before broader enforcement deadlines kick in.
This shift means that organisations can no longer treat compliance as theoretical: even if full legal obligations for high‑risk systems aren’t yet applicable they must already prepare and demonstrate readiness.
Proposed “Digital Omnibus” Changes Could Alter Key Rules
Recent news indicates that the European Commission is considering significant reforms to the AI Act as part of a wider package called the Digital Omnibus. These changes are intended to simplify regulatory obligations, align AI rules with other EU digital laws, and react to industry feedback that some provisions are overly burdensome.

Member states remain divided on how far these changes should go—a tension between easing compliance burdens and retaining strong protections. Some proposals include streamlined requirements for certain categories of AI and clearer implementation timelines. The reforms are attracting both support and criticism from different industry and civil society voices.
Whether these changes will be adopted and in what form, remains a key question for anyone tracking the latest EU AI Act news today.
National Implementation Efforts Are Underway
Beyond EU‑level measures, member states are actively building national structures to enforce and supervise AI compliance. Reports show progress and challenges in establishing competent authorities responsible for oversight, audits and conformity assessments.
This bottom‑up implementation work is vital because enforcement depends not only on EU legislation but also on how effectively individual countries adopt and enforce the rules on the ground.
How EU AI Act News Today Affects Different Stakeholders
Tech Companies and Developers
For tech companies especially those creating general‑purpose AI models or deploying predictive systems the latest developments mean concrete compliance planning is no longer optional. Obligations for transparency, data governance, and risk mitigation are already active for general‑purpose AI after August 2025 and high‑risk deadlines are approaching.
Developers will need to invest in internal compliance resources, documentation workflows and possibly third‑party audits. This translates into operational investments and shifts in product roadmaps, especially for products aimed at the European market.
Businesses Using AI Internally
Companies that use AI internally whether for recruitment, customer support or risk assessment must now evaluate whether those systems fall under high‑risk or other regulatory tiers. For high‑risk classifications, preparatory compliance steps required today will feed into future enforcement.
Failure to prepare could result in costly adjustments later or even restrictions on how AI systems can operate within business processes.
Citizens and Civil Society
From a societal perspective, the EU AI Act news today brings incremental protections into focus. Prohibitions on unacceptable risk systems, transparency obligations for powerful models and enhanced enforcement structures promise greater accountability. Civil society groups often see the Act as a foundation for broader human rights protections in digital environments.

Role of the European AI Office
The newly established European AI Office will play a central role in monitoring and enforcing the AI Act and its responsibilities include coordinating national authorities overseeing compliance audits providing guidance to companies and developers and evaluating emerging AI risks across the European Union.
This office serves as a central reference point for stakeholders seeking clarity on how to interpret and implement the regulation while ensuring that AI systems operate in a manner consistent with European values human rights and ethical standards.
The European AI Office will also offer advisory support for audits and compliance frameworks to assist companies in meeting legal obligations effectively and organizations that engage proactively with the office can receive guidance on best practices for transparency reporting and risk management.
Compliance Requirements for High-Risk AI Systems
High-risk AI systems include technologies deployed in healthcare law enforcement recruitment critical infrastructure and other areas where errors could have serious consequences and companies developing these systems must conduct thorough risk assessments maintain comprehensive technical documentation implement robust human oversight mechanisms and establish continuous monitoring and auditing practices.
Failure to meet these obligations can result in significant fines legal liability and restricted market access and understanding these requirements is crucial for AI developers aiming to operate in the European Union.
Companies must also ensure that all system updates are tracked documented and verified according to the standards set by the EU AI Act while training personnel to maintain compliance across the lifecycle of the AI system and this proactive approach minimizes risk and strengthens the reliability of AI solutions in the European market.
Transparency and Accountability Obligations
The AI Act places strong emphasis on transparency and accountability by requiring developers to disclose AI system capabilities limitations decision-making processes and potential risks and companies must provide clear information to users explaining when they are interacting with AI and how decisions are made.
This transparency is intended to build trust allow users to make informed choices and enable regulators to assess whether AI systems are safe ethical and compliant with EU standards and organizations should establish clear communication protocols and user documentation to fulfill these obligations consistently.
Ongoing monitoring of system behavior and reporting outcomes regularly is also required to maintain transparency and accountability and organizations that implement these practices are better positioned to demonstrate responsible AI use and comply with EU regulations.
Impact on Non-EU Companies
Even companies headquartered outside the European Union are subject to the EU AI Act news today if they provide AI products or services to EU citizens or operate within the European market and non-compliance can lead to financial penalties legal challenges and reputational damage.
These global implications make the EU AI Act one of the most influential AI regulations in the world and companies across North America Asia and other regions are closely monitoring the latest developments in EU AI Act news today to ensure they meet all obligations.
Global businesses should integrate compliance checks into product development cycles to mitigate risks while aligning with ethical AI principles and non-EU companies that adopt these standards early will gain credibility and access to European markets without regulatory obstacles.
How to Prepare for Compliance
Organizations seeking compliance with the EU AI Act should first review the AI Act latest version PDF and understand their AI systems classification and then establish internal compliance frameworks including risk management strategies documentation standards monitoring processes and human oversight protocols.
Companies may also consult legal and technical experts to ensure readiness for audits and inspections once the legislation is fully enforced and proactive preparation reduces legal risk and strengthens the credibility and reliability of AI solutions.
Training employees to understand compliance obligations is essential for readiness while ensuring all internal processes are auditable and companies that prepare thoroughly are more likely to pass inspections and demonstrate ethical AI practices effectively.
Key Benefits of the EU AI Act News Today
The EU AI Act promotes trust in AI systems and encourages innovation under clear legal guidelines and protects fundamental rights of EU citizens and harmonizes regulations across member states and sets a benchmark for ethical AI practices worldwide.
These benefits extend beyond Europe because multinational companies adopting compliant practices contribute to safer and more transparent AI systems globally and align with emerging international standards and investor expectations.
Businesses that embrace compliance early gain a competitive advantage by demonstrating responsibility and ethical AI practices and enhance consumer confidence in their AI products and services and organizations that integrate these practices into operations are better positioned for long-term success.
The Road Ahead: What to Watch Next
Upcoming Deadlines
The phased timeline continues:
- High‑risk AI full requirements become enforceable August 2, 2026.
- Extended transition periods for some regulated products stretch into 2027.
These deadlines are critical and organisations worldwide are adjusting compliance programs accordingly.
Simplification Proposals
The Digital Omnibus reforms could reshape how the AI Act is applied. Stakeholders should monitor legislative discussions closely to understand emerging obligations and timelines.
Enforcement and Penalties
Enforcement momentum is building. Supervisory authorities are preparing to act and fines for non‑compliance can be severe, scaling with company revenue. Real‑world enforcement actions are expected to become more visible as authorities gain experience.
Final Thoughts
The EU AI Act news today reflects a regulatory framework transitioning from policy development to real‑world implementation and enforcement. Preparatory obligations for high‑risk systems are now active and proposed reforms signal continued evolution of the rules. Organisations of all sizes must adapt to a landscape where legal compliance, ethical AI practices, and transparent governance are increasingly non‑negotiable.
As deadlines approach and enforcement matures the EU AI Act continues to shape not only European AI practice but also the global regulatory conversation. Staying informed about EU AI Act news today isn’t just useful it’s essential for navigating the future of artificial intelligence responsibly and effectively.
FAQs
What is the EU AI Act and why is it significant?
The EU AI Act is the first comprehensive legal framework regulating artificial intelligence based on risk. It aims to protect public safety, fundamental rights, and democratic values while guiding innovation responsibly.
Does the EU AI Act apply outside Europe?
Yes. If an AI system is placed on the EU market or its outputs are used within the EU, organisations worldwide must comply with relevant provisions.
What are high‑risk AI systems under the EU AI Act?
High‑risk systems are those that could meaningfully affect people’s health, safety, rights, or livelihoods. Examples include AI in medical diagnostics, automated hiring, or credit scoring systems.
What obligations took effect in 2025?
General‑purpose AI model providers became subject to transparency and documentation requirements starting August 2, 2025. Preparatory obligations for high‑risk systems are now in force as of early 2026.
How often will the AI Act be updated?
The AI Act is designed to be reviewed periodically incorporating technological developments emerging risks and societal needs to ensure continuous protection of users and adherence to ethical AI practices.
Are there penalties for non‑compliance?
Yes. Penalties can reach substantial amounts, including fines based on a percentage of global turnover for serious breaches. Enforcement agencies are preparing to implement these measures.
How can organisations prepare for the EU AI Act?
Organisations should conduct risk assessments for their AI systems, document governance processes, prepare transparency disclosures, and engage with legal and technical compliance expertise.





One Comment